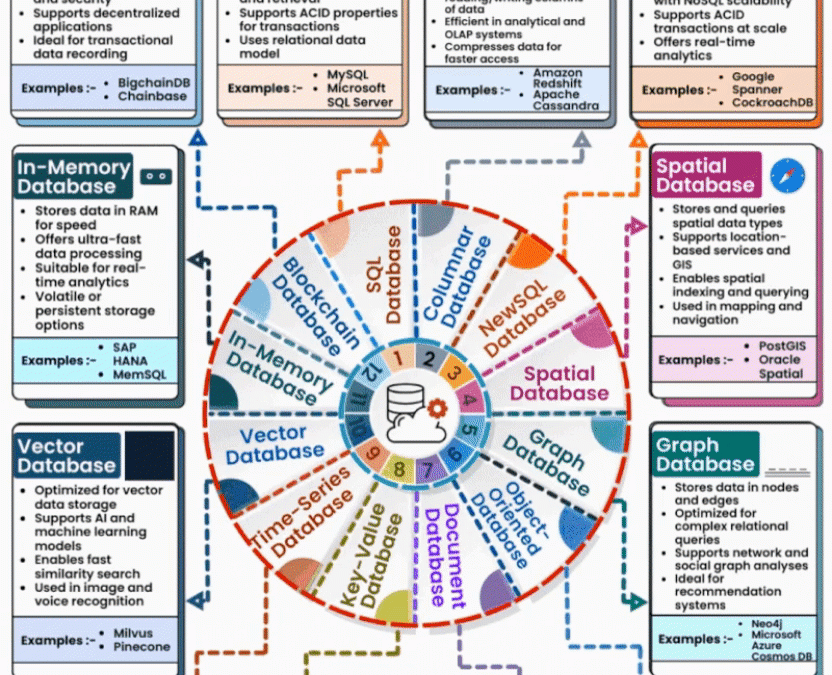
Top Databases Use Cases
In today’s data-driven world, databases play a pivotal role in storing, managing, and retrieving information efficiently. Here are some of the top use cases where databases are instrumental:
Transactional Data Management:
- Transactional databases are essential for managing day-to-day operations of businesses. They handle online transactions, such as purchases, payments, and reservations, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
Analytical Processing:
- Analytical databases are optimized for complex queries and analytics. They are used to analyze large volumes of data to derive insights, make data-driven decisions, and perform business intelligence tasks.
Content Management Systems (CMS):
- CMS databases power content-heavy websites and applications, allowing users to create, manage, and publish digital content seamlessly. They store text, images, videos, and other multimedia assets.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- CRM databases store customer information and interactions, providing insights into customer behavior, preferences, and history. They help businesses build and maintain relationships with customers, personalize marketing efforts, and improve customer service.
Inventory Management:
- Inventory databases track stock levels, orders, and product information in real-time. They enable businesses to optimize inventory levels, manage supply chains efficiently, and prevent stockouts or overstocking.
Geospatial Data Management:
- Geospatial databases store and analyze geographic information, including maps, coordinates, and spatial relationships. They are used in applications such as navigation systems, logistics, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
Time-Series Data Handling:
- Time-series databases specialize in storing and analyzing data points with timestamps, such as sensor data, financial market data, and IoT device telemetry. They enable trend analysis, anomaly detection, and forecasting.
Big Data Processing:
- Big data databases handle massive volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. They support distributed computing frameworks like Hadoop and Spark for processing, analyzing, and deriving insights from large datasets.
E-commerce Platforms:
- E-commerce databases manage product catalogs, customer orders, payment transactions, and inventory levels for online stores. They ensure a seamless shopping experience, secure payment processing, and accurate order fulfillment.
- Healthcare databases store patient records, medical histories, treatment plans, and diagnostic results. They facilitate collaboration among healthcare professionals, ensure patient privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Databases serve as the backbone of modern applications and systems, powering a wide range of use cases across various industries. Understanding the specific requirements and characteristics of each use case is crucial for selecting the right database solution to meet business needs
Keep visiting QuickShare and write to us in the comments below.