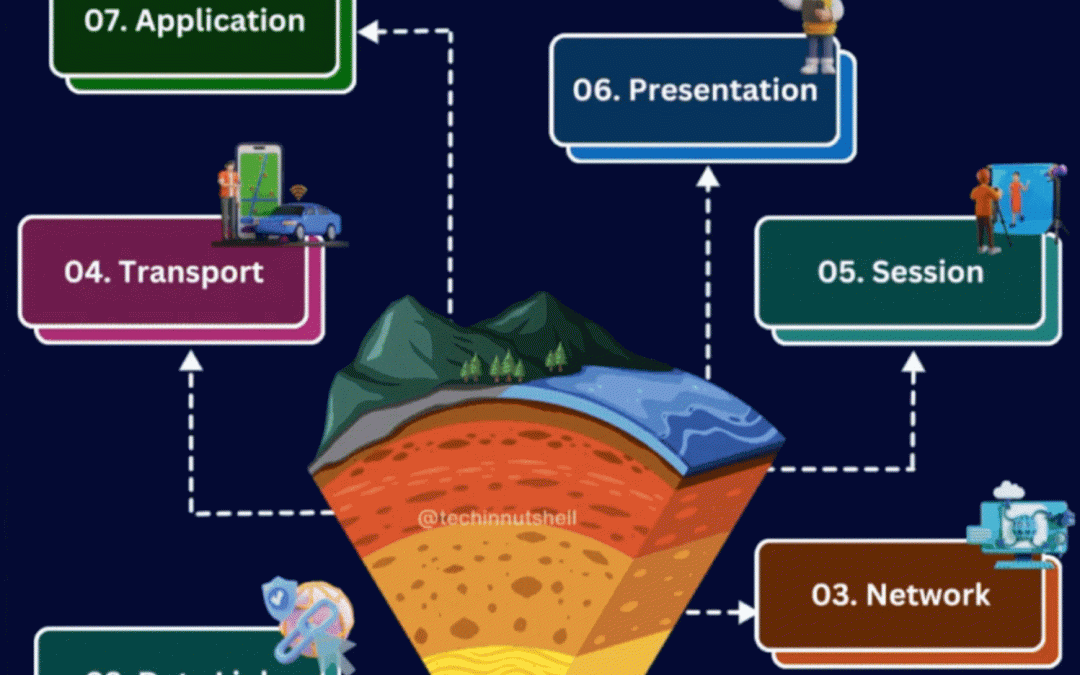
Understanding the OSI Model: Unravelling the Seven Layers
The OSI model, with its seven layers, provides a structured framework for designing and comprehending network functionality.
1. Physical Layer:
The foundation of network communication, dealing with hardware transmission—cables, connectors, and voltages. It defines transmission media, bit rates, and network topology.
2. Data Link Layer:
Forms a reliable link between connected nodes, ensuring error-free data frame transmission. This layer manages MAC addresses and flow control.
3. Network Layer:
Focuses on logical addressing, routing across networks, and congestion management. It assigns IP addresses, determines optimal data paths, and forwards packets.
4. Transport Layer:
Ensures end-to-end communication, managing data segmentation, flow control, and error recovery. It breaks down and reassembles data, regulates flow, and ensures data integrity.
5. Session Layer:
Establishes, manages, and terminates communication sessions. It controls dialogue flow, session initiation, termination, and synchronizes processes.
6. Presentation Layer:
Translates data between the application and lower layers. It manages data format translation, encryption, compression, and ensures readable data for applications.
7. Application Layer:
Interacts with end-user applications, providing network services, user interfaces, and defining application protocols.
Summary
The OSI model serves as a vital guide for network design and understanding. Each layer plays a crucial role, contributing to the efficient flow of data in interconnected systems. This knowledge is essential for network professionals and developers in designing and maintaining modern communication systems.
Keep visiting QuickShare and write to us in the comments below.